Spark 基础知识
Spark
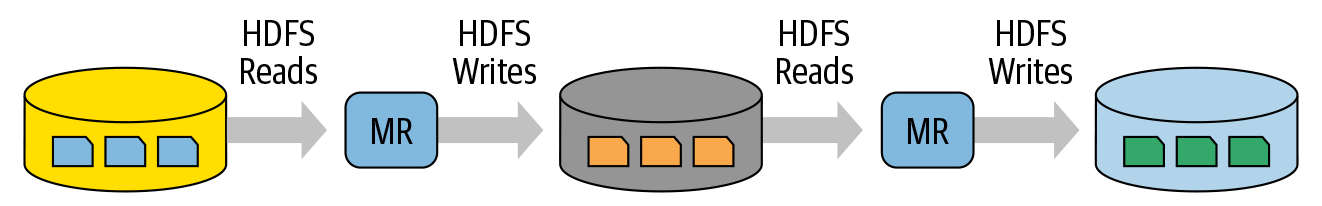
Spark的诞生,源于Hadoop的几个问题:
1、管理较难
这个在学习Hadoop的时候就感受到了,一大堆参数需要调,非常麻烦
2、MapReduce API
需要一大堆模板文件和代码,而且异常处理很难。
3、中间步骤有太多落盘
诚然保存中间结果到磁盘,可以提升可靠性,但大大降低了速度和性能。
4、难以适应多种多样的数据需求
并不是所有任务都可以拆解为Map和Reduce,有些任务比如AI,它当然也可以算作一个Reduce,但这个Reducer该何其地复杂,才能完成哪怕一步的计算。如果是AI训练任务等,则更加困难。
5、缺乏交互性
所有的任务都被预先处理好进入Hadoop集群处理,缺乏交互性
Spark 诞生
Spark 最早由UC Berkeley 的一些研究人员开发,他们认为MapReduce不够效率,而且过于复杂。所以Spark的理念就是:
Simpler,Faster and Easier
早期的Spark就已经能够达到Hadoop MapReduce 10~20倍的性能。
今天已经能达到100倍性能
Apache Spark—a unified computing engine and set of libraries for big data
Unified
Spark被设计为支持各种各样的数据分析任务,比如:
- Simple data
- SQL query
- ML/AI
- Streaming computation
这些操作都是使用同一个计算引擎,同一套API。
Spark的API内部还有一些优化,比如先用SQL query取数据,再调用Spark ML Library,
Spark的引擎会对这些步骤进行合并、优化,减少访问数据的次数来提升性能。
Computing Engine
Spark的定义明确说是一个 computing engine,也就是说它是不包括数据的存储和落盘的部分的。你可以在Azure Storage, Amazon S3, Hadoop HDFS, Kafka, Cassandra等数据载体上用Spark,无论是文件系统,数据库还是消息队列。
相比之下,Hadoop既有计算引擎(MapReduce)又有存储系统(HDFS),使得二者紧紧耦合,难以选择其他的系统(虽然理论上Hadoop也确实可以跑在本地文件系统,S3等之上)。
Libraries
提供一个统一的API接口来完成通用的数据分析任务。
Spark除了内部支持的标准库,还有大量第三方库。
一些知名的Library:
- Spark SQL
- MLlib
- Spark Streaming/Structured Streaming
- GraphX
Spark Application
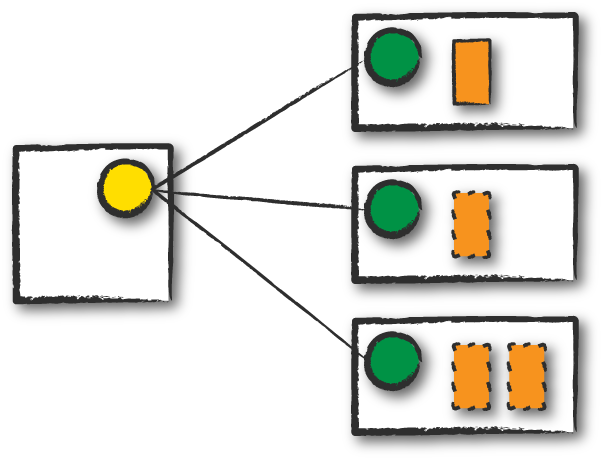
包含Driver process和Executors
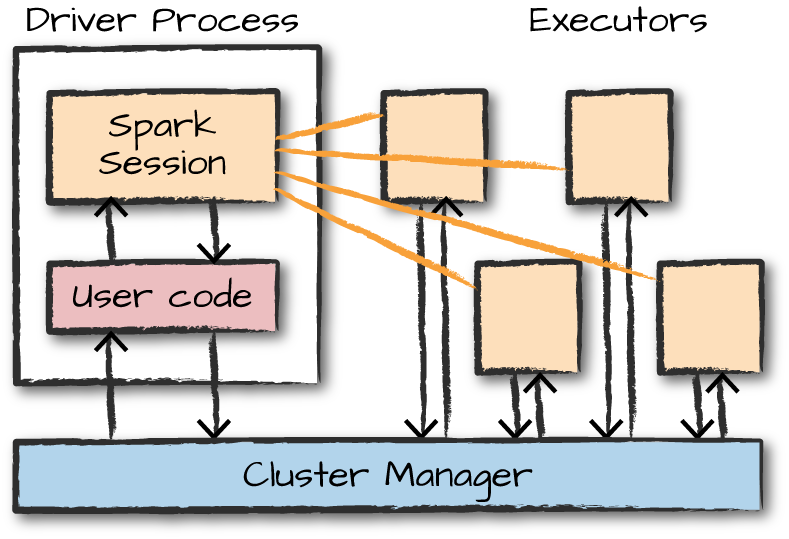
Spark Driver负责控制用户交互和协调executors之间的工作。
Executors负责具体被分配到的工作。
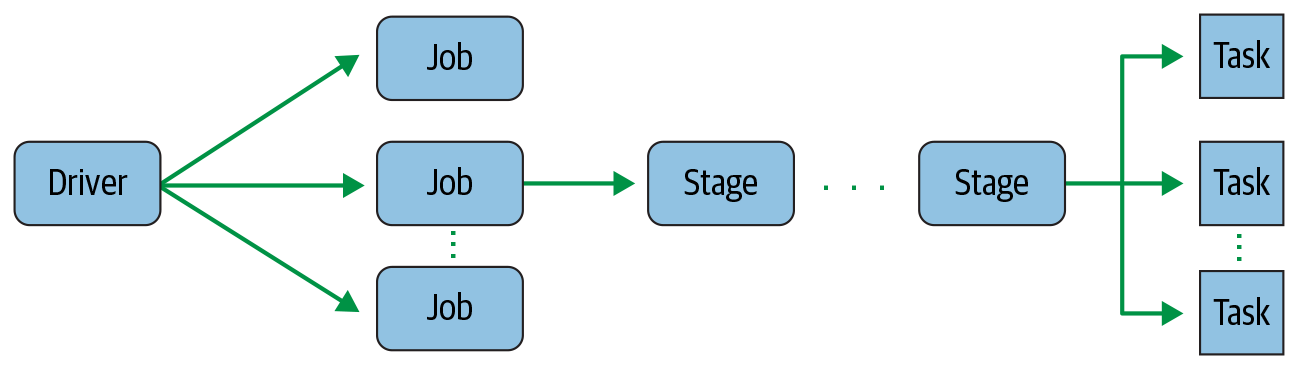
每个Executor执行的,就是Spark Job。
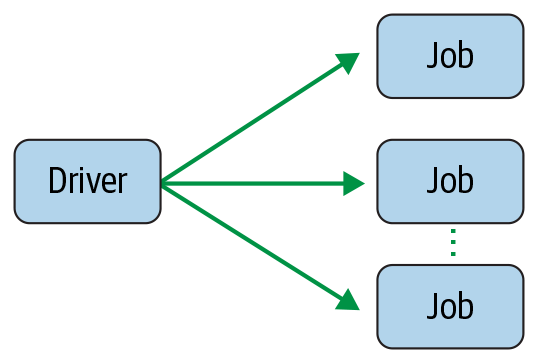
每个Job包含多个Stage,每个Stage包含多个Task
Cluster Mode
Cluster Mode 是最常见的提交任务的方式:
用户提交JAR/Python Script/xx Script -> Cluster manager在Node上启动Driver process和Executor process
Client Mode

和Cluster Mode 不同的地方在于,Client 所在的机器(也就是任务提交的机器)会维护driver process,然后cluster manager维护executor process。这些机器也被称为Gateway machines或Edge nodes,是可以处在集群之外的。
Local Mode
学习时用,在本地运行
Lifecycle
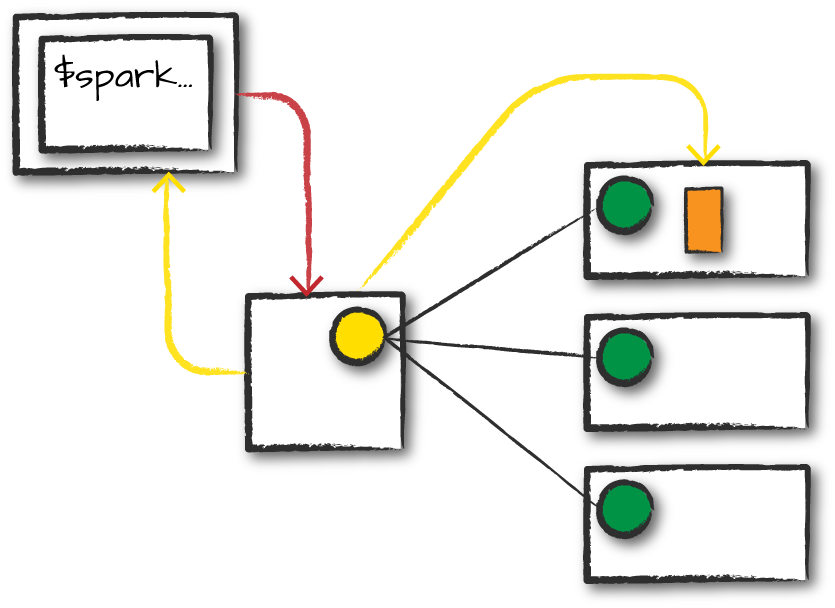
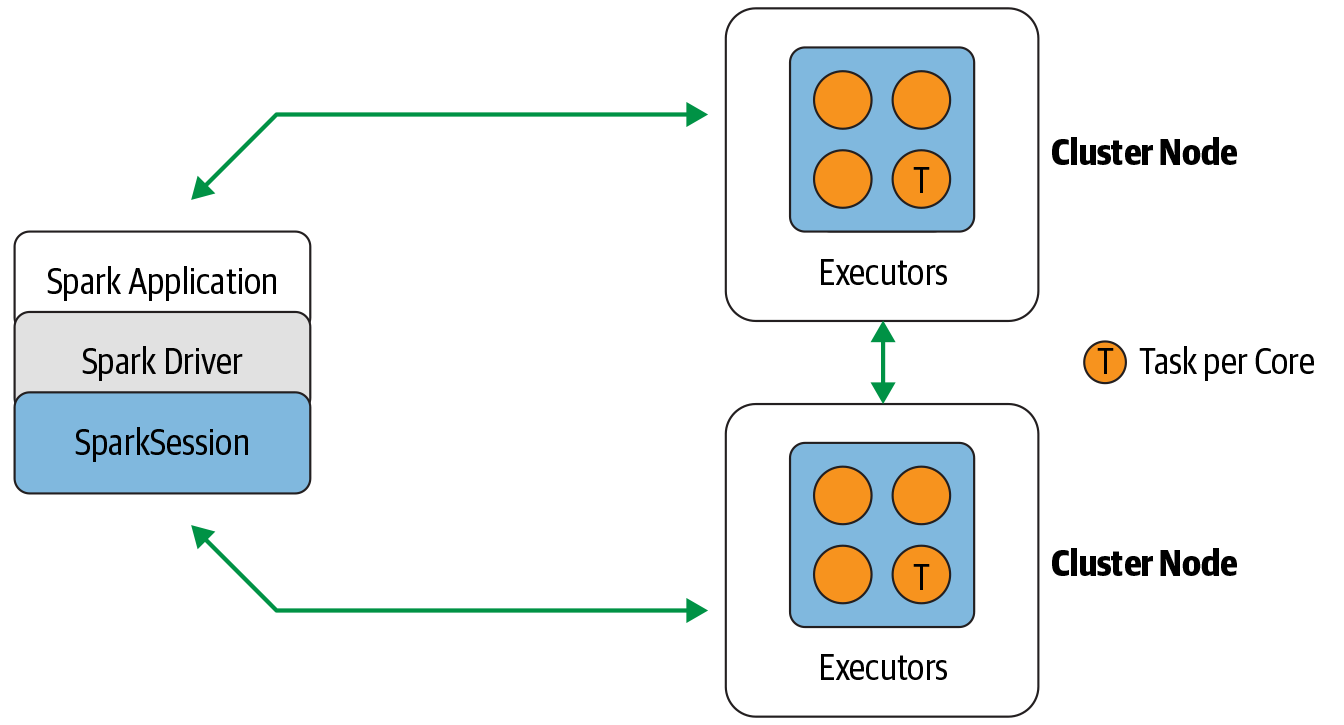
首先客户提交任务,为Spark Driver Process申请资源。然后Cluster Manager会将Driver放在集群中的某一个node上。Driver开始执行代码,代码中包含SparkSession的初始化逻辑,会和集群交互来在节点中分布Executor进程。Driver负责调度,Workers内部自主通信。
一个Spark Job包含多个Stage,通常Spark会试着让同一个Stage执行更多的任务。通常来说,应该让任务的分区数量大于集群的Executor数量,来提升效率
spark.conf.set("spark.sql.shuffle.partitions", 50)
Pipelining就相对好理解,比如先执行map,再执行filter,在执行map,这三个操作在Spark中会被优化在一个stage中完成,中途不落盘而是在内存中计算,来提升效率。
DataFrame
DataFrame就是一个类似表格的数据结构,有列与行。
Spark的DataFrame和原生的区别在于,能够跨多个节点,而不是在单一节点上。
可以将Pandas的df转为Spark的df
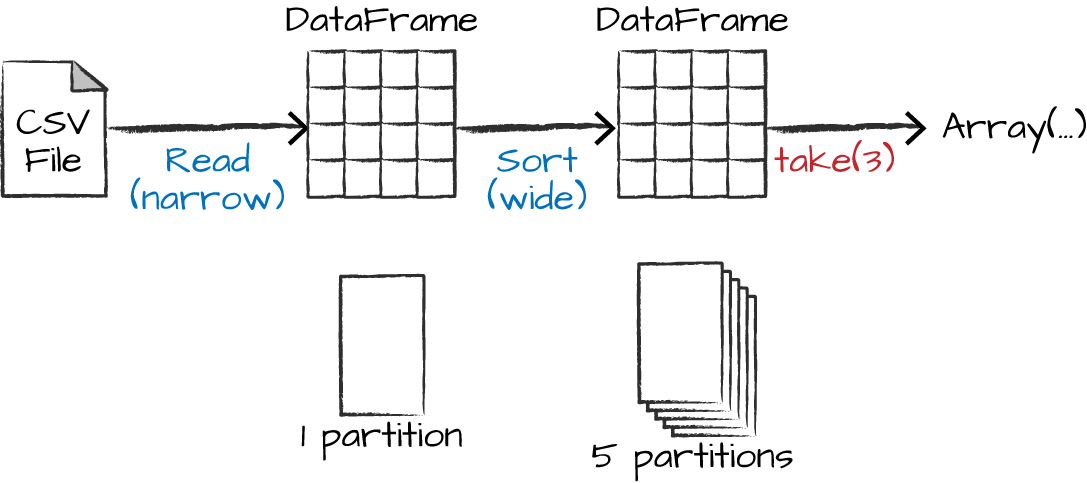
Partitions
每个Partition包含总数据中的若干行子数据,存在一台物理机器上。
如果只有一个Partition,或者只有一个Executor,都无法并行完成任务,只有多Partition多Executor才能真正并行
这部分分区不需要人为指定,但是有底层API
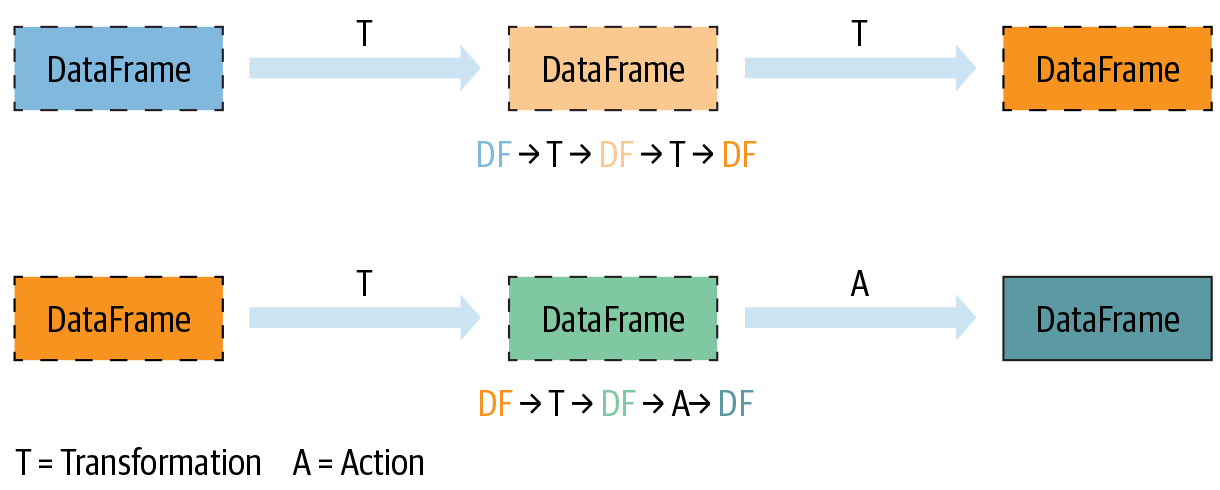
Transformations
# in Python
divisBy2 = myRange.where("number % 2 = 0")
Narrow dependency(Narrow Transformation)
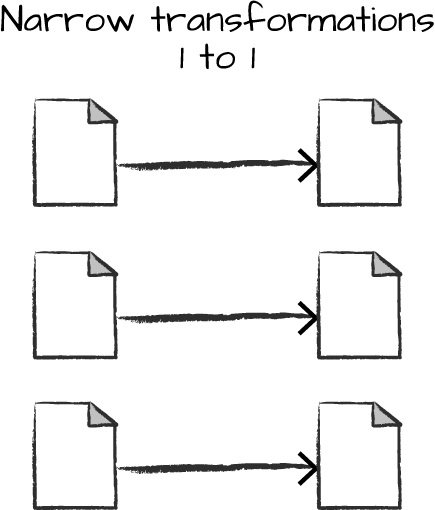
对任意一个输入,只有一个输出,称为Narrow Dependency。对这样的操作,Spark会进行Pipelining,所有操作都在内存中进行。
Wide Dependency
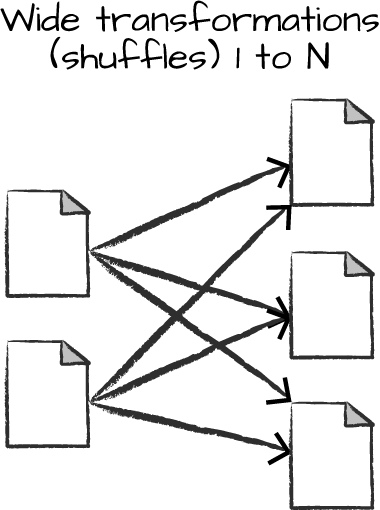
对Shuffle操作,Spark会在集群内部交换Partition,结果会写入磁盘。
Actions
- Actions to view data in the console
- Actions to collect data to native objects in the respective language
- Actions to write to output data sources
如:取得一个DataFrame的记录条数
divisBy2.count()
一些Transformation和Actions:
| Transformations | Actions |
|---|---|
orderBy() | show() |
groupBy() | take() |
filter() | count() |
select() | collect() |
join() | save() |
Lazy Evaluation
在对数据进行操作时,并不立即修改,而是建立一个plan,包含多个操作。
直到最后,编译这个plan,然后优化后再一起执行。
比如Predicate Pushdown,这类在数据库经常用到的优化,就会在这个时候做,大大加快处理速度。
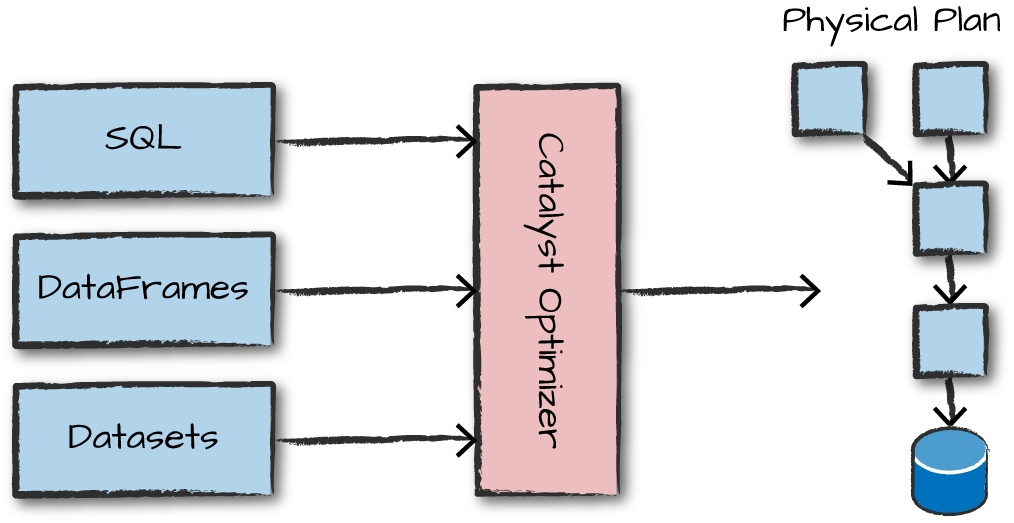
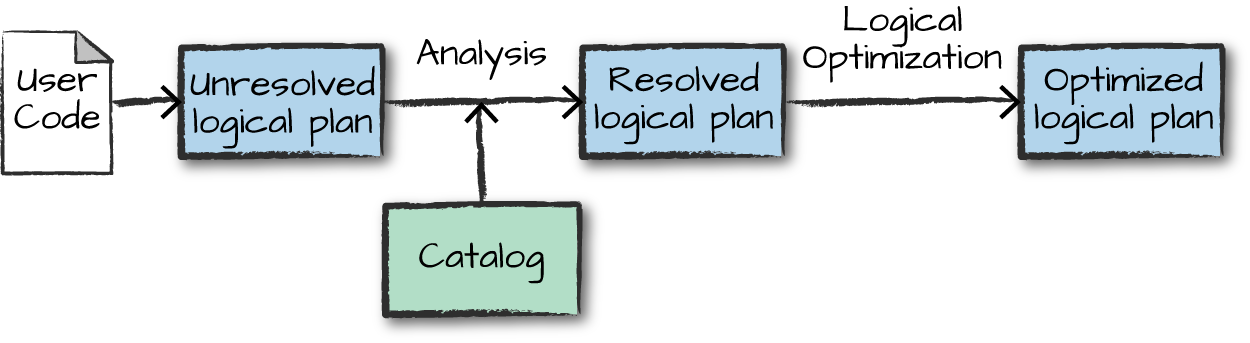
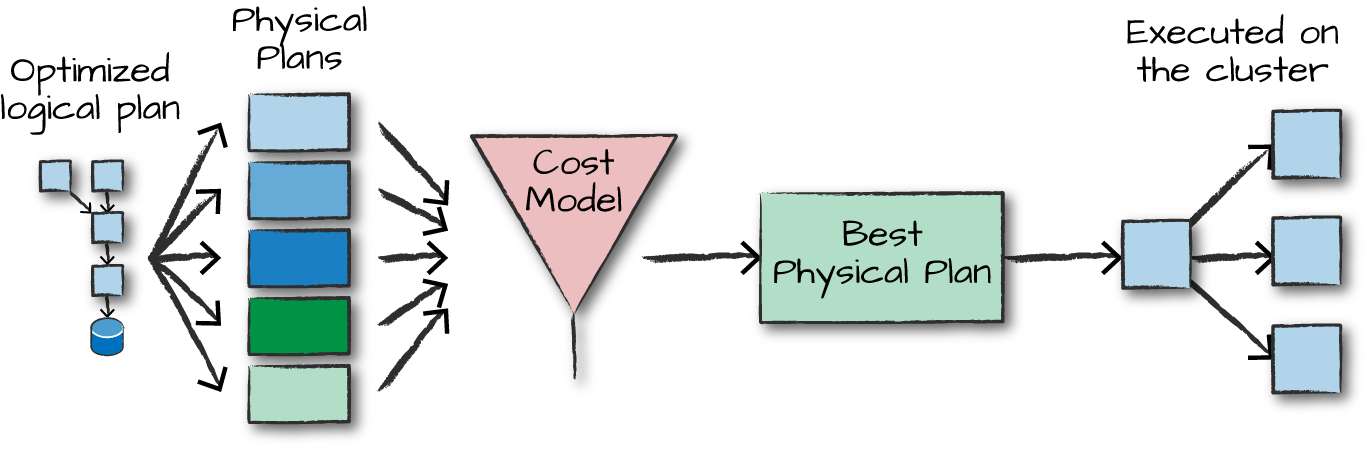
Logical Planning and Physical Planning
RDD

参考nsdi12-final138.pdf
In short, an RDD represents an immutable, partitioned collection of records that can be operated on in parallel. Unlike DataFrames though, where each record is a structured row containing fields with a known schema, in RDDs the records are just Java, Scala, or Python objects of the programmer’s choosing.
High Level API:
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
from pyspark.sql.functions import avg
# Create a DataFrame using SparkSession
spark = (SparkSession
.builder
.appName("AuthorsAges")
.getOrCreate())
# Create a DataFrame
data_df = spark.createDataFrame([("Brooke", 20), ("Denny", 31), ("Jules", 30),
("TD", 35), ("Brooke", 25)], ["name", "age"])
# Group the same names together, aggregate their ages, and compute an average
avg_df = data_df.groupBy("name").agg(avg("age"))
# Show the results of the final execution
avg_df.show()
对应的Low Level RDD操作:
# Create an RDD of tuples (name, age)
dataRDD = sc.parallelize([("Brooke", 20), ("Denny", 31), ("Jules", 30),
("TD", 35), ("Brooke", 25)])
# Use map and reduceByKey transformations with their lambda
# expressions to aggregate and then compute average
agesRDD = (dataRDD
.map(lambda x: (x[0], (x[1], 1)))
.reduceByKey(lambda x, y: (x[0] + y[0], x[1] + y[1]))
.map(lambda x: (x[0], x[1][0]/x[1][1])))
创建RDD
spark.range(10).rdd
数据类型
| Data type | Value assigned in Scala | API to instantiate |
|---|---|---|
ByteType | Byte | DataTypes.ByteType |
ShortType | Short | DataTypes.ShortType |
IntegerType | Int | DataTypes.IntegerType |
LongType | Long | DataTypes.LongType |
FloatType | Float | DataTypes.FloatType |
DoubleType | Double | DataTypes.DoubleType |
StringType | String | DataTypes.StringType |
BooleanType | Boolean | DataTypes.BooleanType |
DecimalType | java.math.BigDecimal | DecimalType |
| Data type | Value assigned in Python | API to instantiate |
|---|---|---|
BinaryType | bytearray | BinaryType() |
TimestampType | datetime.datetime | TimestampType() |
DateType | datetime.date | DateType() |
ArrayType | List, tuple, or array | ArrayType(dataType, [nullable]) |
MapType | dict | MapType(keyType, valueType, [nullable]) |
StructType | List or tuple | StructType([fields]) |
StructField | A value type corresponding to the type of this field | StructField(name, dataType, [nullable]) |
Spark SQL
spark.read.json("/data/flight-data/json/2015-summary.json")\
.createOrReplaceTempView("some_sql_view") # DF => SQL
spark.sql("""
SELECT DEST_COUNTRY_NAME, sum(count)
FROM some_sql_view GROUP BY DEST_COUNTRY_NAME
""")\
.where("DEST_COUNTRY_NAME like 'S%'").where("`sum(count)` > 10")\
.count() # SQL => DF
Stream Processing
Micro Batches(DStream)
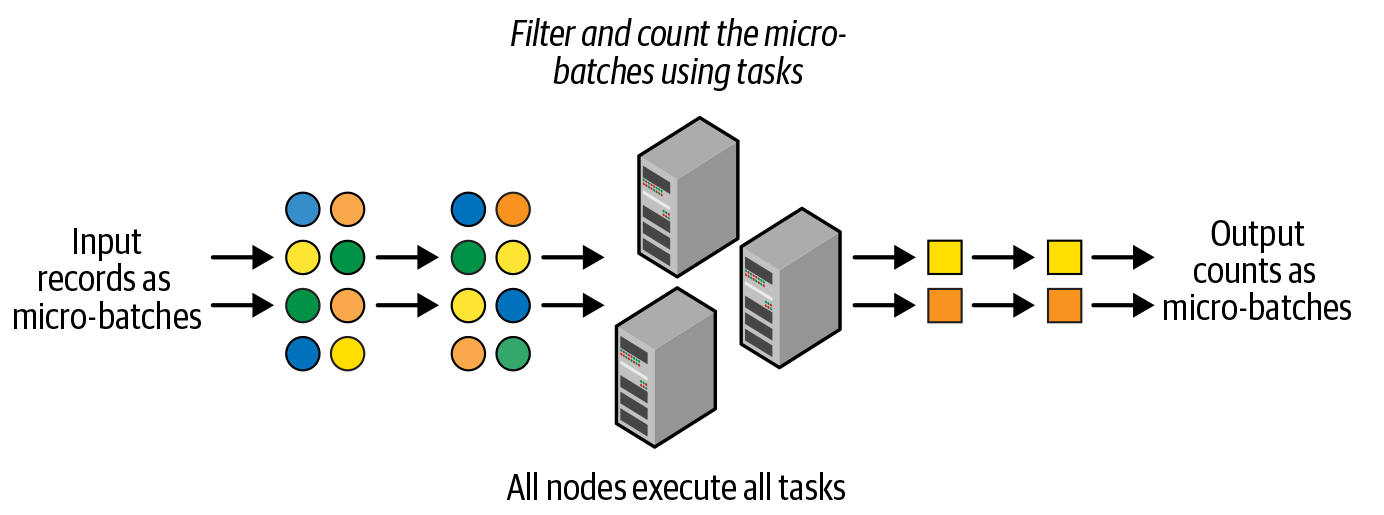
秒级延迟,但大大降低单机处理数据的开销
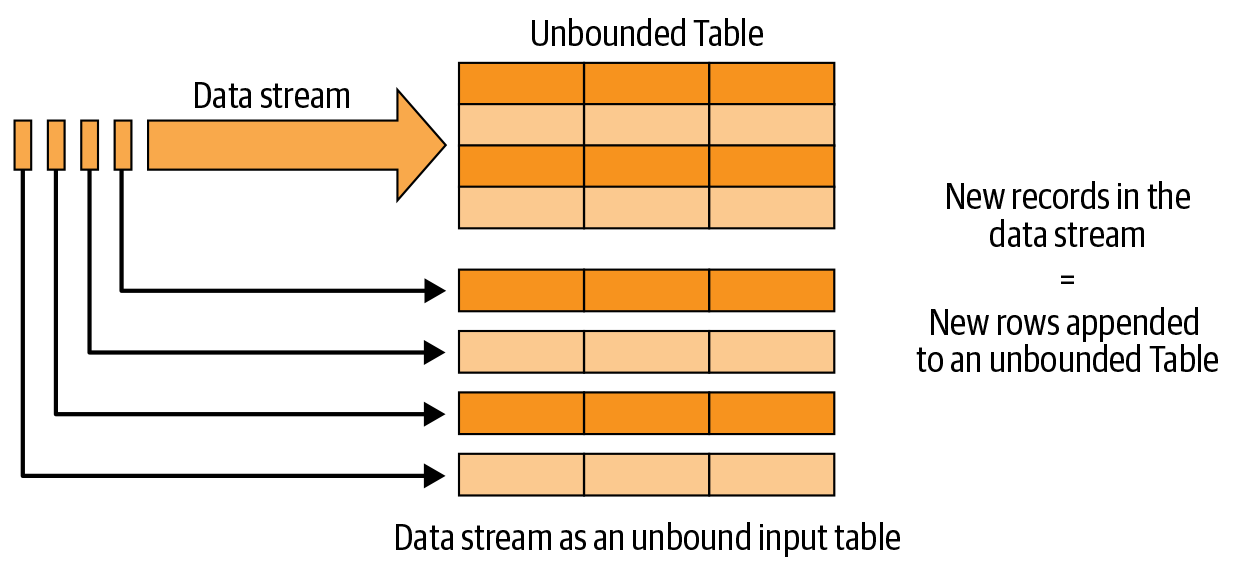
Incremental Execution
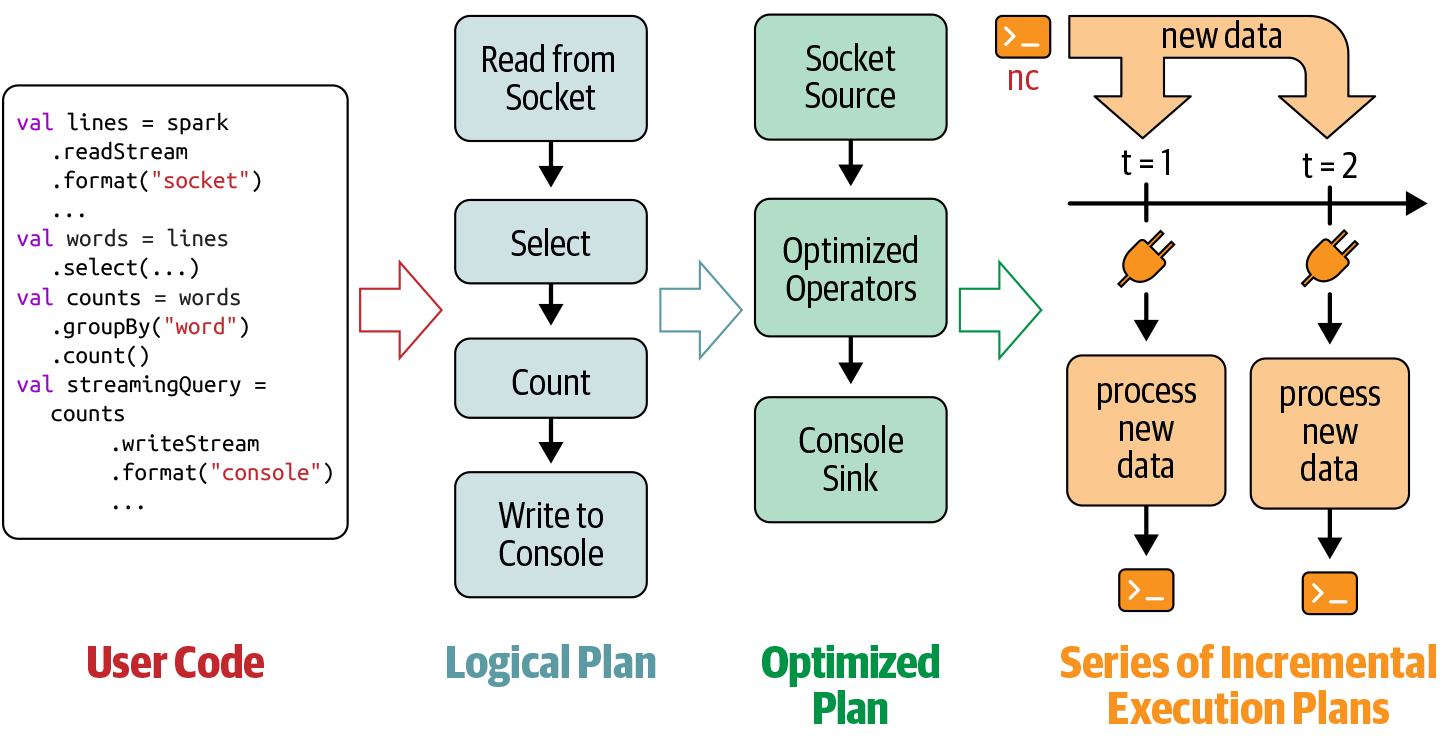
# In Python
inputDF = (spark
.readStream
.format("kafka")
.option("kafka.bootstrap.servers", "host1:port1,host2:port2")
.option("subscribe", "events")
.load())
streamingQuery = (counts
.selectExpr(
"cast(word as string) as key",
"cast(count as string) as value")
.writeStream
.format("kafka")
.option("kafka.bootstrap.servers", "host1:port1,host2:port2")
.option("topic", "wordCounts")
.outputMode("update")
.option("checkpointLocation", checkpointDir)
.start())
性能优化
总体来说,文件最好使用二进制格式存储,而不是csv格式,因为文件最好能够被Split成多个分块来让不同的进程读取。这也牵出了之前Hadoop遇到的同样问题,可分割压缩格式。Zip就是一个典型的无法分割的压缩格式,使用Zip格式意味着只有一个进程能从头到尾读取它的数据,不能从中分段读取。相对来说,gz, bz2, lz4就都有办法可以分割,提升读取效率。
避免UDF(User-Defined Functions),尤其是在Python和R语言中,脚本语言本身解析速度就有限,尽量使用Structure API
Stream Processing
优势:
低延迟,增量更新结果,高效率(与Batch processing 相比)
挑战:
乱序数据
复杂状态
高吞吐
Exact once
低延迟
Structured Streaming
Structured streaming的目的在于复用已有的Batch API(DataFrame, Dataset, SQL),它将每一条新数据当作表中的一条新纪录。
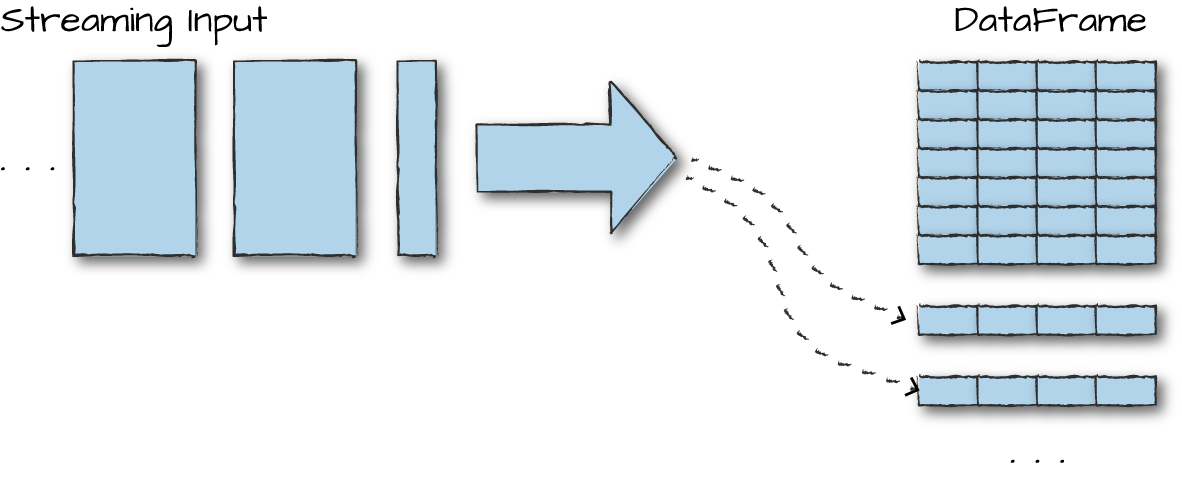
从Input读取数据,然后写到Sink中。
最典型的数据存取源就是Apache Kafka。
安装
brew install scala
brew install apache-spark